If you’ve ever looked at a company’s financial report, you might have seen the term EBIT and wondered what it means. The EBIT meaning can seem confusing at first because it’s a technical term used in finance and accounting. EBIT is an important measure for understanding a company’s profitability before interest and taxes. Whether you’re a business student, investor, or just curious about finance, knowing what EBIT is can help you interpret financial statements and make better business decisions. This article explains the meaning of EBIT in simple English, with clear examples, real-life applications, and common mistakes. Updated for 2026, it’s designed for beginners and anyone learning business or finance terminology.
What Does “EBIT Meaning” Mean?
EBIT stands for Earnings Before Interest and Taxes.
In simple terms:
EBIT = Profit a company makes from operations before paying interest and taxes
It shows the company’s operating performance without the effects of financing or taxation.
EBIT Meaning in Simple English
EBIT measures how much money a company earns from its core operations.
Formula:
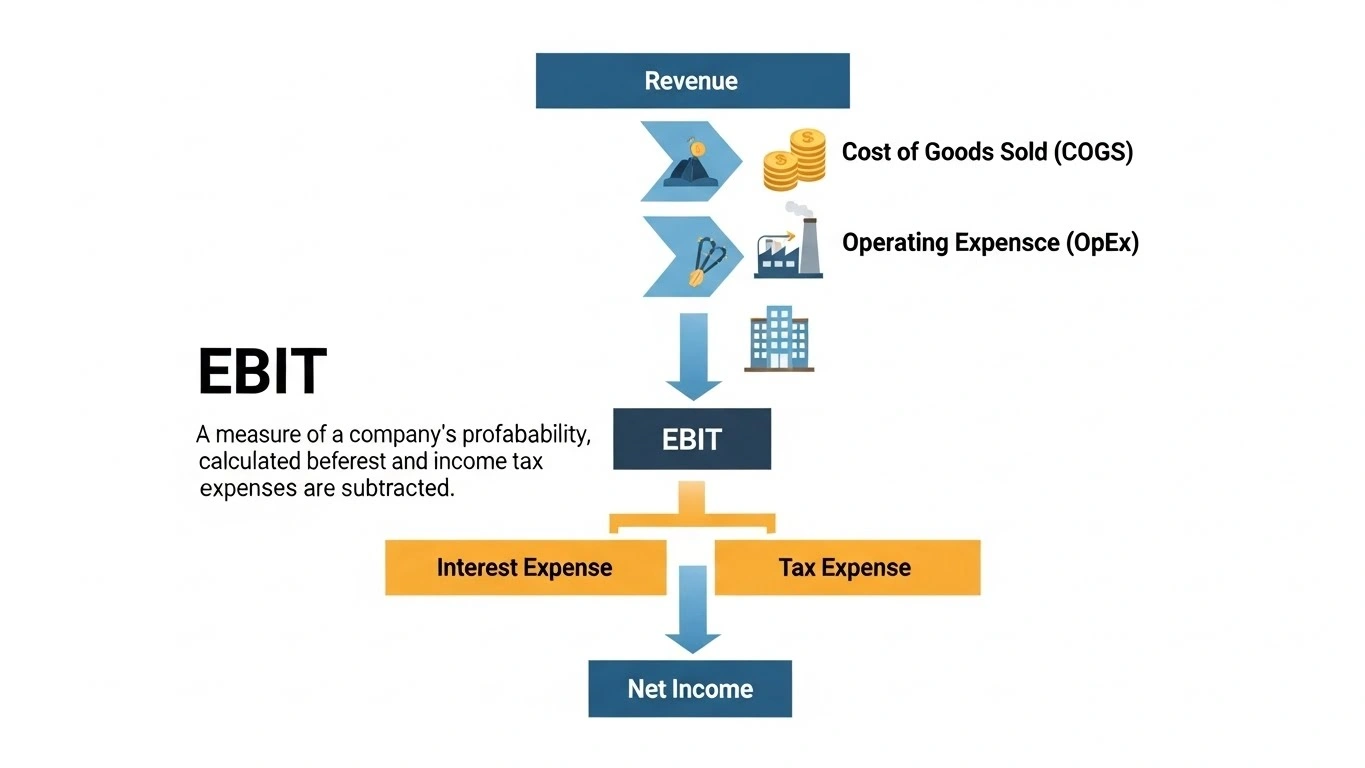
EBIT = Revenue – Operating Expenses
or
EBIT = Net Income + Interest + Taxes
It’s sometimes called operating profit.
Why EBIT Meaning Is Important
EBIT is widely used in finance because it:
Shows operational efficiency
Helps compare companies without tax or debt differences
Assists investors in understanding profitability
Supports business decisions like budgeting or investment
Example:
Two companies earn the same revenue, but one has more debt. EBIT helps compare performance without considering interest.
EBIT vs Other Profit Measures
Understanding EBIT is easier when you compare it with other financial metrics.
EBIT vs EBITDA
EBITDA = Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization
Difference: EBITDA ignores depreciation/amortization; EBIT includes them
EBIT vs Net Income
Net income = Profit after all expenses, interest, and taxes
EBIT ignores interest and taxes, focusing on operational profit
EBIT vs Operating Income
Sometimes EBIT and operating income are used interchangeably
Operating income typically comes from core business only, excluding non-operating items
How People Use “EBIT Meaning” in Real Conversations
EBIT is used mostly in business, investment, and accounting discussions.
Common Situations
Company financial reports
Investor analysis
Business meetings
Accounting courses
Online finance articles
Example Sentences
“The company’s EBIT increased by 15% this quarter.”
“Investors look at EBIT to gauge operational performance.”
“EBIT excludes taxes, so it’s easier to compare internationally.”
Real-Life Examples of EBIT Meaning
Example 1: Simple Company
Revenue: $500,000
Operating Expenses: $300,000
EBIT = $500,000 – $300,000 = $200,000
Explanation:
The company earned $200,000 from its operations before interest and taxes.
Example 2: Including Taxes and Interest
Net Income: $150,000
Interest: $20,000
Taxes: $30,000
EBIT = $150,000 + $20,000 + $30,000 = $200,000
Explanation:
This method calculates EBIT starting from net income.
Example 3: Comparing Companies
Company A EBIT: $500,000
Company B EBIT: $300,000
Even if Company B pays less tax or interest, Company A’s operational performance is better.
Example 4: Startup Scenario
Startup revenue: $50,000
Expenses: $40,000
EBIT = $10,000
Shows operational profit before financing costs.
Example 5: Investor Analysis
“EBIT margin is 25%”
Indicates that for every $100 of revenue, $25 comes from operations before interest and taxes
Common Mistakes and Misunderstandings
Confusing EBIT With Net Income
Mistake:
Thinking EBIT = Profit after tax
Correction:
EBIT ignores taxes and interest. Net income includes them.
Forgetting Non-Operating Income
Mistake:
Including non-operating gains or losses in EBIT
Tip:
EBIT focuses on operational earnings
Using EBIT Without Context
Mistake:
Comparing EBIT of companies in different industries blindly
Tip:
Compare EBIT margins, not absolute values
Confusing EBIT With EBITDA
Mistake:
Using EBIT and EBITDA interchangeably without checking depreciation
Correction:
EBITDA ignores depreciation/amortization; EBIT includes it
Related Financial Terms
Revenue – Total income from sales
Operating Expenses – Costs of running business
Net Income – Profit after all costs, interest, and taxes
EBITDA – Profit before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization
Operating Margin – EBIT as a percentage of revenue
These terms often appear together in financial reports.
FAQs
What does EBIT meaning mean in simple words?
EBIT means earnings before interest and taxes; it shows operational profit.
Is EBIT the same as operating income?
Almost. EBIT often equals operating income but can include non-operating items in some reports.
Why is EBIT important for investors?
It shows how profitable a company is from core operations, ignoring tax and financing differences.
How do you calculate EBIT?
EBIT = Revenue – Operating Expenses or EBIT = Net Income + Interest + Taxes
Can EBIT be negative?
Yes. If operating expenses exceed revenue, EBIT is negative, showing a loss from operations.
Conclusion
The EBIT meaning is simple once you understand it: it’s the profit a company earns from its operations before interest and taxes. It’s a key measure for investors, business owners, and finance students to evaluate operational performance without external factors affecting the numbers. Understanding EBIT helps you interpret financial reports, compare companies, and make smarter business decisions.